Table Of Contents

Why SAS?
Being a SAS Professional, I can tell you why SAS. I would say it’s a bit tiny subject; however, it is unique, competitive and leading within the analytics world. SAS is the main statistical tool certified by the FDA and IIRC.
SAS is a Statistical Analysis System, i.e. a collection of software program tools created by the SAS Institute. SAS programming has numerous applications including the analysis of multivariate, predictive analysis, management of data and business intelligence.
Statistics show that 70% of analytics jobs are in SAS Programming, followed by R and Python. It is an ever-evolving technology according to industry needs and is one major factor in its favor.
SAS Job Profiles
Below are some of the job profiles you can take up as a SAS “professional”:
SAS Analyst
SAS Programmer
Customer Analytics Manager
Decision Analyst
There is a huge scope of SAS for freshers. Banks are heavily using SAS, as are Insurance & other Financial Services companies like HSBC, Citi, JP Morgan, & Wells Fargo.
So, it’s sensible to grab the opportunity if you get it by some means to learn and work on SAS technology.
How to learn SAS Programming online for free?
You do not want to spend a whopping six months learning SAS. You can follow the 6-week learning guide and become a proficient SAS programmer.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to get started in case you are a beginner.

Step “1”: Download and install SAS Studio
SAS University Edition can be downloaded for free and is available for everyone. You can download it on your PC or use it from the Cloud.
Below are the articles you can refer to download and set up SAS.
Step “2”: SAS Interfaces
Before writing any code, you must first become acquainted with the SAS interface.
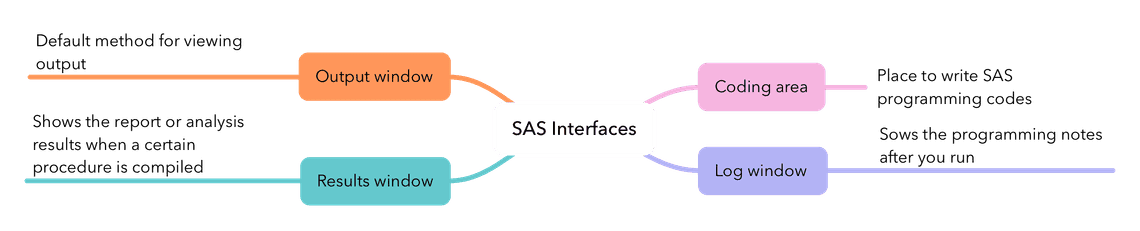
Fortunately, the SAS interface is pretty easy to understand. Below is a brief of every part of the interface.
Coding Area
The coding space is positioned in the middle of the SAS Studio interface. This is the place you can write SAS programming codes.

LOG Window
The LOG window shows the programming notes after you run.
the program. It provides details about the code execution and whether there is an issue with the program and other useful Notes.

Results Window
The RESULTS window shows the report or analysis results when a procedure is compiled.

Output Window

SAS Libraries
SAS Library may be seen as the folder that contains all the SAS files and datasets.
Learn more by referring to the article below.

Folders
Folders allow you to organize your SAS programs and quickly access your saved SAS programs.

Step “3”: Learn the SAS Library and Data Sets
SAS Library is the folder that comprises all of the SAS information. Learn about temporary and permanent libraries and how to create and permanent library.
SAS Programming – Basics of SAS Programming Language
Step “4”: Learn How to Create a Data Set
SAS data set is the file that contains all the data. You must understand how to create data sets. Learn to create a SAS dataset and the options available in SAS.
Step “5”: Learn SAS Functions
Now that you have a stable foundation of SAS data sets, it is time to begin learning how to manipulate data.
One of the methods to manipulate data is to use the built-in SAS functions.
Learn about the character, numeric and data functions in SAS. A simple example is using the SUM function to add up all of the numeric values.
You can learn about SAS functions from the below link.
Step “6”: Learn SAS Variables
In SAS, six attributes define every of the SAS “variables”:
Name
Label
Length
Type
Format
Informat
Learn about variable attributes from SAS Variable Attributes - SAS Help Center
Learn about the formats and informats in SAS from Ultimate Guide to SAS Formats and Informats.
Step “7”: Learn to read and write the SAS dataset.
Data usually comes from an external source. It is important to learn how to read data from an external file.
Learn to import data in SAS from Import data into SAS.
Step “8”: Learn Data Manipulations
SAS programs often involve data manipulation. Sorting and concatenation data are a few examples of data manipulations.
Step “9”: Learn Data Analysis
SAS is among the world’s best statistical analysis software programs. Below are some examples of the data analysis steps that are commonly used.
Step “10”: Learn Proc SQL
Proc SQL is an advanced programming step generally used when working with data in a relational database. However, it can achieve identical results as the standard data step with greater efficiency.
Learn the basics of PROC SQL from A comprehensive guide to PROC SQL in SAS (15 + Examples)
Step “11”: Learn SAS Macro and Advanced SAS Techniques
SAS macro is another advanced programming technique that enables you to perform dynamic value substitution and automate repetitive tasks.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, SAS is a powerful tool that can be used to explore and manipulate information. But to use it effectively, it is important to understand its structure, and how to navigate the syntax you will be working with.
Hopefully, by following this course, you can now have that basic knowledge and start building programs for your own data sets.

