Table Of Contents
Finding the maximum value in a group is a common task in data analysis. In SAS, there are several ways to accomplish this task. In this blog post, we will explore some of the different methods available.
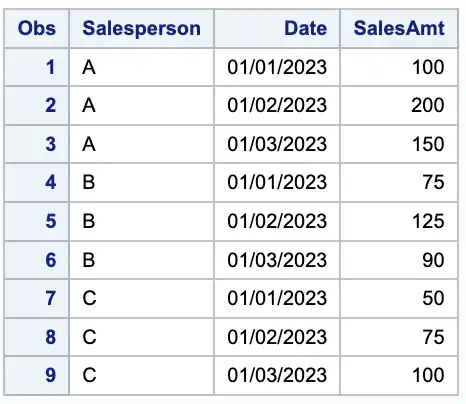
First, let’s set up some sample data. Suppose we have a dataset of sales transactions that includes the sales amount, the date of the transaction, and the salesperson who made the sale. We want to find the highest sales amount for each salesperson.
data sales;input Salesperson $ Date :mmddyy10. SalesAmt;format Date mmddyy10.;datalines;A 01/01/2023 100A 01/02/2023 200A 01/03/2023 150B 01/01/2023 75B 01/02/2023 125B 01/03/2023 90C 01/01/2023 50C 01/02/2023 75C 01/03/2023 100;run;
Method 1 Proc SQL Group By
One way to find the maximum sales amount for each salesperson is to use PROC SQL. Here’s an “example”:
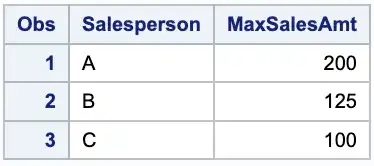
proc sql;create table max_sales asselect Salesperson, max(SalesAmt) as MaxSalesAmtfrom salesgroup by Salesperson;quit;
This creates a new table called max_sales that includes the salesperson and their maximum sales amount.
Method 2 Proc SQL Self Join
One way to find the maximum value in a group using PROC SQL is to use a self-join. In this approach, we join the table to itself using a common key and then select the maximum value for each group. Here’s an example using the same sales dataset as “before”:
proc sql;create table max_sales asselect s1.Salesperson, max(s2.SalesAmt) as MaxSalesAmtfrom sales s1inner join sales s2on s1.Salesperson = s2.Salespersongroup by s1.Salesperson;quit;
In this code, we first create a table called max_sales. Then, we select the salesperson and the maximum sales amount by joining the sales table to itself using the inner join clause and the on clause to specify the common key. Finally, we group the results by the salesperson using the group by clause.
Note that we use different aliases (s1 and s2) to refer to the sales table in the join statement, and we use the max function to find the maximum sales amount for each group.
Method “3”: Using a Data Step and BY-Group Processing
A third way to find the maximum sales amount for each salesperson is to use a data step with BY-group processing. Here’s an “example”:
data max_sales;set sales;by Salesperson;if first.Salesperson then MaxSalesAmt = SalesAmt;else if SalesAmt > MaxSalesAmt then MaxSalesAmt = SalesAmt;if last.Salesperson;drop SalesAmt;run;
This creates a new table called max_sales that includes the salesperson and their maximum sales amount. Note that we use the by Salesperson statement to specify the grouping variable and the if first.Salesperson and if last.Salesperson statements to identify the first and last observations within each group.
Method “4”: Using PROC SUMMARY
Another way to find the maximum sales amount for each salesperson is to use PROC SUMMARY. Here’s an “example”:
proc summary data=sales;var SalesAmt;class Salesperson;ways 1;output out=max_sales (drop=_type_ _freq_) max(SalesAmt)=MaxSalesAmt;run;
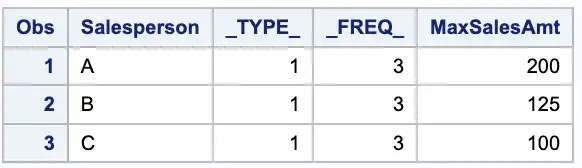
WAYS 1 statement to select only the TYPE 1 in the output.
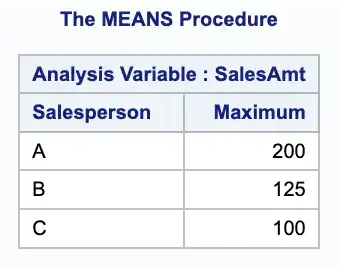
Method “5”: Using PROC MEANS
PROC MEANS is another useful procedure in SAS for finding summary statistics, including the maximum value in a group. Here’s an example of how to use PROC MEANS to find the maximum sales amount for each salesperson in the same sales “dataset”:
proc means data=sales nonobs max maxdec=0;var salesamt;class salesperson;run;
Method “6”: Using PROC UNIVARIATE
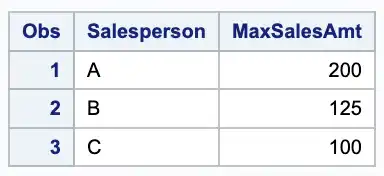
PROC UNIVARIATE is another SAS procedure that can be used to find the maximum value in a group. Here’s an example of how to use PROC UNIVARIATE to find the maximum sales amount for each salesperson in the same sales “dataset”:
proc univariate data=sales noprint;class Salesperson;var SalesAmt;output out=max_sales max=MaxSalesAmt;run;proc print;
In this code, we use the class statement to specify the grouping variable and the var statement to specify the variable we want to summarize. We also use the output statement to create a new table called max_sales that includes the salesperson and their maximum sales amount.
Method “7”: Using PROC RANK
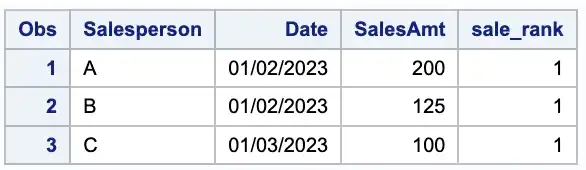
PROC RANK is a SAS procedure that can be used to rank data within groups. By using PROC RANK with the ties=LOW option, we can assign the same rank to tied values and then use the where statement to select only the top-ranked observations within each group, which will give us the maximum value in each group. Here’s an example of how to use PROC RANK to find the maximum sales amount for each salesperson in the same sales “dataset”:
proc sort data = SALES;by Salesperson;run;proc rank data=sales out= test2(where=(sale_rank=1)) ties=low descending;by Salesperson;var SalesAmt;ranks sale_rank;run;