Table Of Contents

SAS date and time are essential topics in SAS because SAS date and time have unique characteristics. SAS dates are not numeric, not character variables. When displayed, it resembles a character, although it is stored as a number.
A SAS date begins from January 1, 1960, and has a value of 0. Before this dates are negative numbers and positive numbers after this date. SAS Formats are used to display values in various formats. There are several different SAS date formats that you can apply and make the dates readable.
[ Recommended “Reading”: [The Yearcutoff System Option in SAS](https://www.9to5sas.com/yearcutoff-system-option/) ]
Reading SAS dates
You can use SAS date informats to read SAS dates from an input file. A date informat tells SAS to read dates as specified in the informat and ensure dates are stored correctly as date values while the value itself is stored as a number of days since January 1, 1960.
Here is an example showing what happens when you use the wrong date format.
data one;input dt mmddyy10. dt2 monyy.;datalines;04-22-2020 APR20;run;
This output will show a missing numeric value (.) for the dt variable. In this case, you need to read the SAS log to see what might have gone wrong while reading the SAS date. Here is the log message indicating a NOTE.
"NOTE": Invalid data for dt in line 72 1-10. "NOTE": Invalid data for dt2 in line 72 11-15. "RULE": ----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5----+----6----+----7----+----8----+----9----+----0 72 04-22-20 APR2020 dt=. dt2=. _ERROR_=1 _N_=1
So, what went wrong?
The first step in investigating these errors is to check whether you have used the correct date format to read the date values.
For example, if the date informat used is mmddyy10. and the data value given is in the format of ddmmyy10.
The date format is correct, but the raw data value is eight digits wide instead of 10. Therefore, if you examine the actual column shown in the rule, you will see a mismatch where SAS is expecting a date in the format of mmddyy10.
That means the width of the date informat for the dt1 variable is ten, and the monyy format specifies the format width of 5. (3 for month name and 2 for the year).

The above illustration shows a mismatch between the width of the column specified by the informat variable dt1 and the actual date value. The dt2 variable expects the date to begin from column 12 but begins from column 9. This is because only two digits are specified for the year part in dt1 variable.
How can you fix this?
You have identified a mismatch in the date informat and the column’s width; you can fix this in two ways.
The first solution is to use formatted input with a column pointer. This way, you can tell SAS explicitly which column and variable should begin.
input dt mmddyy10. @10. dt2 monyy.;
Another method is to use the correct width of the informat according to the raw data. That is if you use mmddyy8. Then, SAS will read the dates correctly.
Creating SAS date constants
You can create SAS date constants using the form.’ddmmmyy'd or 'ddmmmyyyy'd. The quotes are necessary, as well as the letter ‘d’.
“Example”:
data three;dt1='20APR20'd;dt2='20APR2020'd;put _all_;run;
The log below with the date value in a numeric “format”: the number of days since January 1, 1960.
dt1=22025 dt2=22025 ERROR=0 N=1
Importing dates from Excel to SAS
Generally, PROC IMPORT is preferred while importing date from excel to SAS. You must ensure that dates are correctly imported in SAS if the Excel date is stored as ‘General Format’.
Excel default date starts from January 1, 1900, and SAS dates start from January 1, 1960. While SAS can include negative number dates before January 1, 1960, excel cannot.
Therefore, a date before January 1, 1900, will be missing unless the field is stored as a character variable.
Here is the snapshot input file in xlsx format.
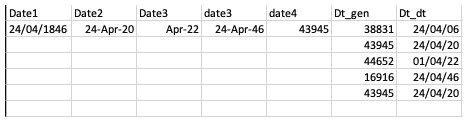
To import the excel file in SAS, we will submit the following code.
proc import datafile= "/folders/myfolders/dates.xlsx"dbms = xlsx out=four replace;run;
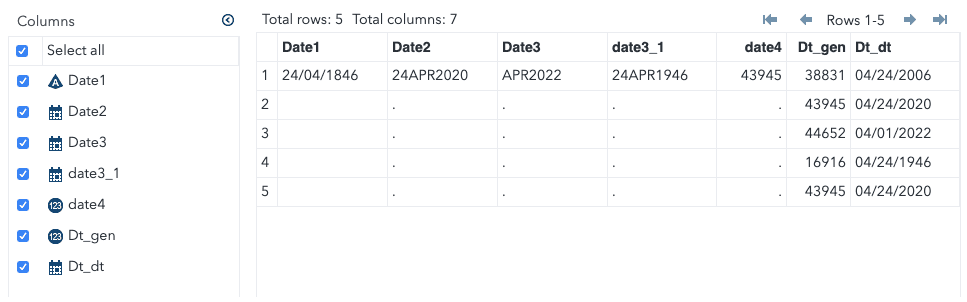
The date1 variable is a character date format, and the date4 variable is the number of days since the excel start date.
You can use the input function to convert the character date to the actual date value followed by the date informat in SAS.
So, what happens when you try to convert date1 and date4 to SAS date format?
data inp;set four;date1 = input(date1,ddmmyy10.); /*converting character date to sas numeric date*/format date4 date1 dt_gen date9.;run;
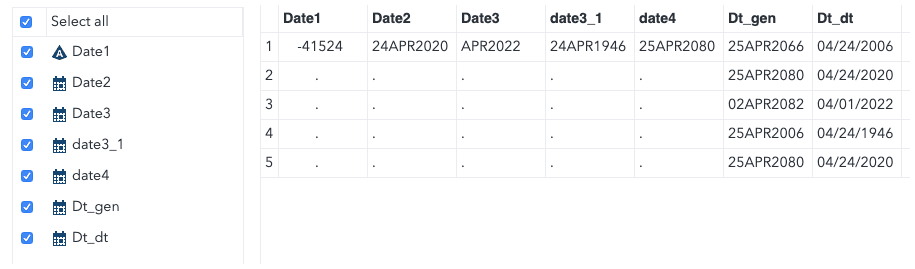
We were able to convert dt_gen from numeric date to SAS, but the years are not correct. This is because Excel stores the number, and SAS imports that number.
Since there is a difference in the default dates between SAS and Excel, you must convert the date and time variable of character dates to SAS dates using the formula below. Only use this formula if the excel date is on or after January 1, 1900.
SAS date = Excel date - 21916SAS Time = Excel time * 86400;SAS date and Time = (Excel date time - 21916) * 86400
data inp;set four;s_date1 = input(date1,ddmmyy10.);sas_dt_gen = dt_gen-21916;format s_date1 date4 sas_dt_gen date9.;run;
Now, date1 and dt_gen dates have been converted to SAS dates with correct values.
You need not be required to subtract 21916 from the date1 as because
Now, date1 and dt_gen dates have been converted to SAS dates with correct values.
You need not be required to subtract 21916 from the date1 because 24/04/1846 is before January 1, 1900.

SAS dates Formats
For displaying SAS dates, you need to use SAS date formats. As discussed, the SAS dates are stored as the number of days sing January 1, 1960, which is not helpful for readability.
Just as SAS date informats are used to read dates, Formats are used for displaying SAS date values
SAS date formats also end with period-like informats. Some of the frequently used SAS date formats are as below.
| SAS Date Format | Default width | Range | Example | Result | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATE. | 7 | 5-9 | DATE9. | 24APR20 | ddmmmyy, ddmmmyyyy, or dd-mmm-yyyy. |
| DAY. | 2 | 2-32 | DAY. | 24 | Day of the month. |
| DDMMYY. | 8 | 2-8 | DDMMYY10. | 24/04/2020 | ddmmyy or dd/mm/yy.\dd is the day of the month.\/ is the separator.\mm is integrer month.\yy is 2/4 digit year |
| DDMMYYX. | 8 | 2-10 | DDMMYYC10. | “24”:“04”:2020 | ddmmyy or ddxmmxyy\dd is day of the month.\x is a specified separator. * ❶\mm is integer month.\yy is 2/4 digit year. |
| DOWNAME | 9 | 1-32 | DOWNAME3. | Friday | name of the day of the week. |
| MMDDYY. | 8 | 2-10 | MMDDYY10. | 04/24/2020 | mmddyy mm/dd/yy\mm is integer month.\/ is the separator.\dd is the day of the month.\yy is 2/4 digit year |
| MMDDYYX. | 8 | 2-10 | MMDDYYD10. | 04-24-2020 | mmddyy mmxddxyy\mm is integer month\x is a specified separator.\dd is the day of the month.\Yy is 2/4 digit year. |
| MMYYX. | 7 | 5-32 | MMYYD. | 04-2020 | mmyy mmxyy\mm is Integer Month\x is separator.\yy is 2/4 digit year |
| MMYY. | 7 | 5-32 | MMYY6. | 4M20 | mmMyy\mm Integer month.\M is the character separator |
| MONAME. | 9 | 1-32 | MONAME1. | A | Date values as the name of the month. |
| MONTH. | 2 | 1-21 | MONTH. | 4 | Month (1 through 12) of the year |
| MONYY. | 5 | 5-7 | MONYY7.; | APRIL2020 | mmmyy or mmmyyyy\mmm is the first three letters of the month name.\yy or yyyy is a 2/4 digit year |
| WEEKDATE. | 29 | 3-37 | WEEKDATE15. | Fri, Apr 24, 20 | day-of-week, month-name dd, yy (or yyyy)\dd is day of the month(Integer).\yy or yyyy is 2/4 digit year |
| WEEKU. | 11 | 3-1200 | WEEKU3. | W16 | Week number in decimal format by using the U algorithm. *❷ |
| WEEKV. | 11 | 3-1200 | WEEKV6. | 20W17 | Week number in decimal format by using the V algorithm. *❸ |
| WEEKW. | 11 | 3-200 | WEEKW. | 2020-W16-05 | Week number in decimal format by using the W algorithm. *❹ |
| WEEKDAY. | 1 | 1-32 | WEEKDAY. | 6 | date value as the day of the week (where 1=Sunday, 2=Monday, and so on). |
| WEEKDATX. | 29 | 3-37 | WEEKDATX20. | Fri, 24 Apr 2020 | day of the week in the form of day-of-week,\dd month-name yy (or yyyy).\dd is day of the month(Integer).\yy or yyyy is 2/4 digit year |
| WORDDATE. | 18 | 3-32 | WORDATE. | April 24,2020 | month-name dd, yyyy. |
| WORDDATX. | 29 | 3-37 | WORDDATX. | 24 April,2020 | dd month-name yyyy. |
| YEAR. | 4 | 2-32 | YEAR2. | 20 | Date values as the year. |
| YYMM. | 7 | 5-32 | YYMM5. | 20M04 | yyMmm\yy is 2/4 digit year\M is the character separator to indicate that the month number follows.\mm is an integer that represents the month. |
| YYMMX. | 7 | 5-32 | YYMMS. | 2020/04 | yymm or yy-mm.\yy 2/4 digit year.\x is a specified separator.\mm is integer month. |
| YYMMDD. | 8 | 2-10 | YYMMDD6. | 200424 | yyMmm\M is a character separator to indicate that the month number follows the M\year as 2 or 4 digits. |
| YYMMDDX. | 8 | 2-10 | YYMMDDB. | 20 04 24 | yymmdd or yy-mm-dd\x - seperator |
| YYMON. | 7 | 5-32 | YYMON5. | 24 APR | yymmm or yyyymmm.\yy is 2/4 digit year.\mmm is the name of the month (3 Characters) |
| YYQ. | 6 | 4-32 | YYQ4. | 07Q1 | yyQq\yy is 2/4 digit year\Q is an integer (1,2,3 or 4) representing the year’s quarter. |
| YYQX. | 6 | 4-32 | YYQS32. | 2020/2 | yyq or yy-q\yy is 2/4 digit year\x is a specified separator.\Q is an integer (1,2,3 or 4) representing the year’s quarter. |
| YYQR. | 8 | 6-32 | YYQRS8. | 2020/II | yyQqr\qr is a roman numeral (I, II, III, or IV) representing the quarter of the year. |
| YYQRX. | 8 | 6-32 | YYQRC6. | “20”:II | yyqr or yy-q\yy is 2/4 digit year.\x is a specified separator. QR is a roman numeral (I, II, III, or IV) representing the year’s quarter. |
SAS Date Formats
❶ The x in the format name represents the special character that separates the year and the month. This special character can be a hyphen (-), period (.), slash (/), colon (:), or no separator.
- C separates with a colon.
- D separates with a hyphen.
- N indicates no separator.
- P separates with a period.
- S separates with a forward slash.
❷ Algorithm U calculates SAS date by using the number of weeks within the year. For example, Sunday is the first day of the week. The number of week values is represented in 0-53.
❸ Algorithm V calculates the number of weeks considering Monday as the starting day of the week and is represented in the range between 01-53. Weeks that begin on a Monday and week 1 of the year include January 4 and the first Thursday of the year. If the first Monday of January is 2,3, or 4, the preceding days are considered as part of the last week of the previous year.
❹ Algorithm W uses the current year as the year expression. If the input does not contain a day expression, then the first day of the week is used as the day expression. It calculates the number of weeks within the year, and Monday is considered the first day of the week. The week’s number is a decimal number in 0-53.

